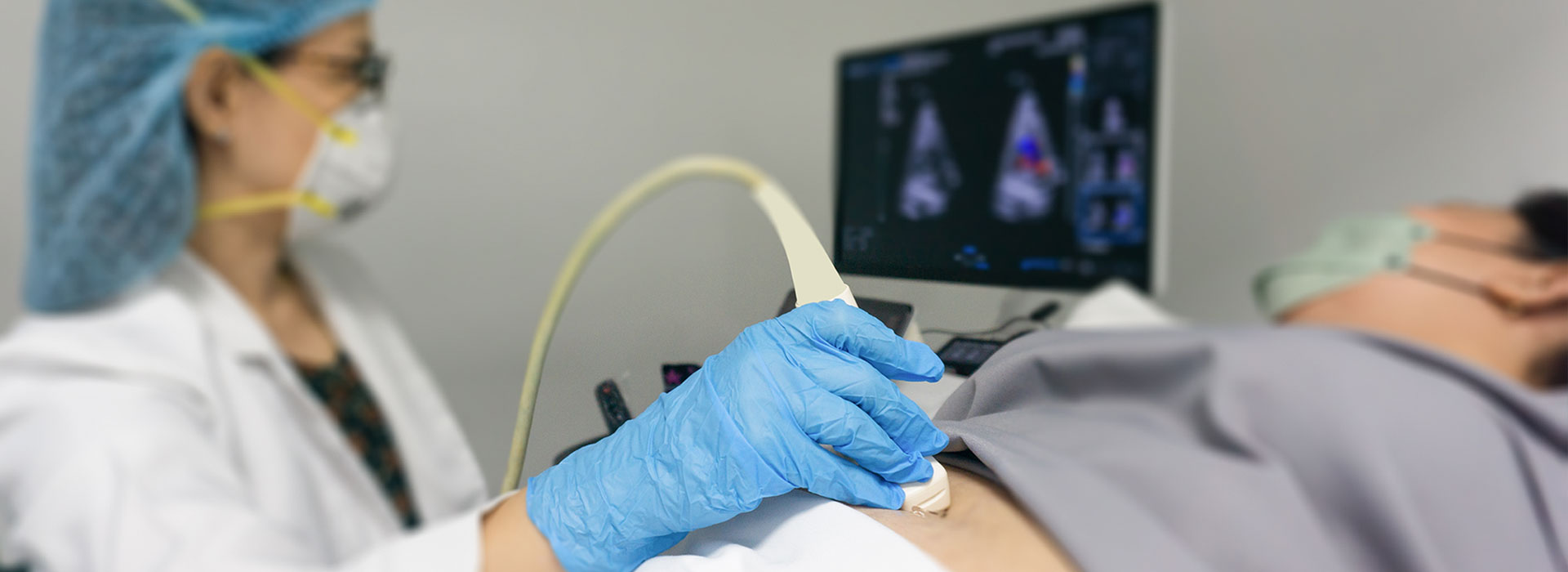
A Fetal Echocardiogram, also known as a fetal echo, is a non-invasive ultrasound test that evaluates the heart's structure and function of an unborn baby. It is typically performed during the second trimester of pregnancy, at about 18 to 24 weeks of pregnancy, and takes approximately 30 min to 2 hours. The test can detect major problems with the developing baby's heart walls, valves, blood vessels, and heart pumping strength. There are two main methods to perform a fetal echocardiogram: Abdominal ultrasound and transvaginal ultrasound. Fetal echocardiograms are often recommended for women with risk factors such as a family history of heart problems, maternal diabetes, or suspected chromosomal abnormalities. Early detection of congenital heart disease before birth has many advantages, and diagnostic accuracy for detecting complex CHD with a fetal echocardiogram is as high.